France and Belgium will be arriving on our stores and on Steam on October 31st, and their arsenals are ready to be deployed against their Warsaw Pact counterparts.
Have a look at some of the most important units that will be under your direct control.

FRANCE
AML-90 Armored Car: In the history of AFVs, there have been few that have been so successful or so extensively employed as the Panhard AML armoured car. Designed on a small, lightly armoured 4×4 chassis, AML-90 is a fast, long-ranged, and reliable vehicle with excellent reconnaissance capability. It showed that a lightweight armoured car, armed with a 90mm main gun, could successfully deal with tanks despite an obvious lack of protection, using speed to achieve confusion and effective flanking fire. Since 1959 AMLs have been marketed on five continents; several variants remained in continuous production for half a century. These have been operated by fifty-four national governments and other entities worldwide, seeing regular combat even today.
AMX-13 Light Tank: The AMX-13 was designed in the immediate aftermath of the Second World War but the production run in a range of several thousand units lasted as late as 1987. It was originally intended as a light tank suitable for air transport, as its role was to serve as a fire support vehicle for paratroopers. It was an ambitious and far-sighted departure from conventional tank design with a number of unusual solutions so it comes as no surprise it found a ready export market as well as being a critical part in the French Army arsenal. Its basic hull design lent itself to the development for more than a hundred different variants, some of them included self-propelled guns, anti-aircraft systems, APCs, and ATGM versions. French designers progressively modernised, and indeed reinvented, the AMX-13 and enabled it to claim to be one of the most successful armoured vehicle programmes of the post-war period. It proved its worth in numerous small wars worldwide in the service of twenty-five countries.
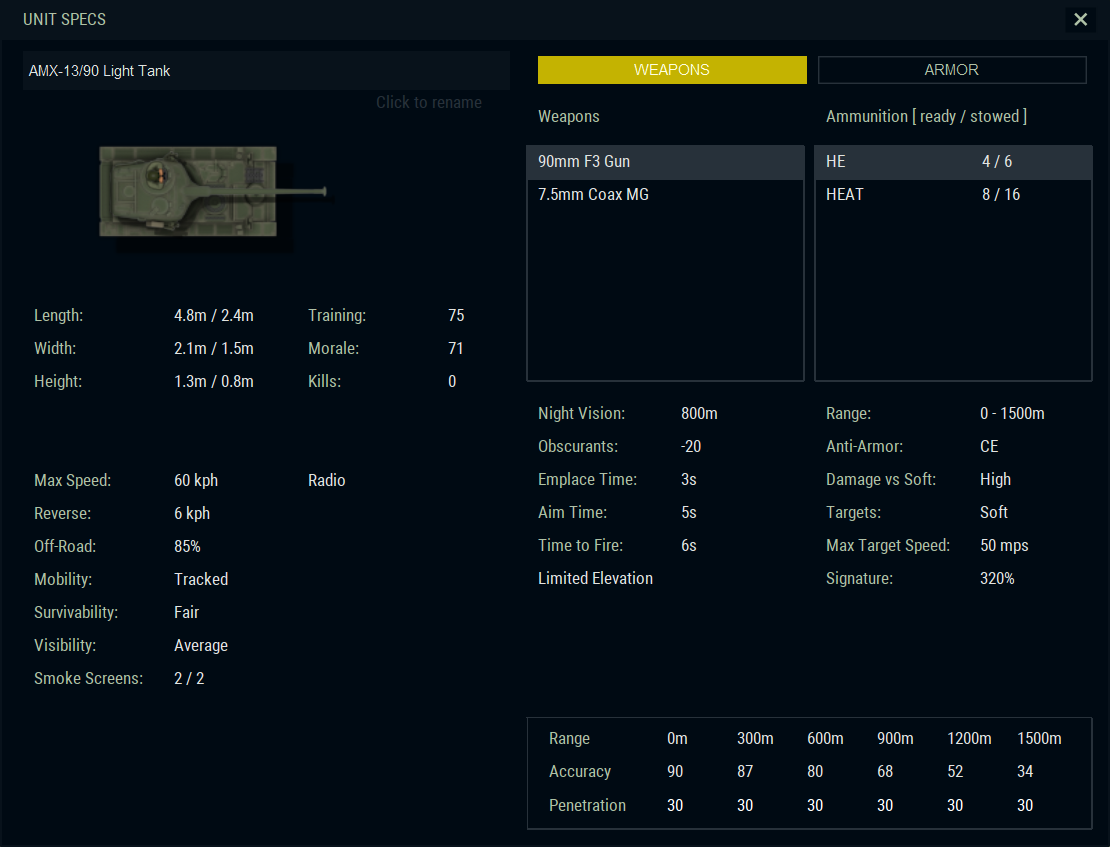
ERC-90 Sagaie: The ERC-90 Sagaie started as a private venture aimed at the export market. It was developed by Panhard in the latter half of the 1970s as a heavier, six-wheeled successor to highly successful AML range of armoured vehicles. Recognizing the need for a cost-effective light armoured vehicle that could defeat more modern tanks, like the Soviet T-72, Panhard designed a new turret which mounted the long barrel F4 90mm smooth-bore cannon. Initially rejected by the French Army in favour of more advanced, but also heavier and costlier AMX-10RC, it was eventually adopted for Fast Deployment Force for overseas military missions, mainly in Africa or the Middle East. The Sagaie is an armoured reconnaissance vehicle first and foremost, with the added secondary role as a tank-destroyer. The ERC-90 series proved to be a resilient and sturdy vehicle and saw action in several conflicts.
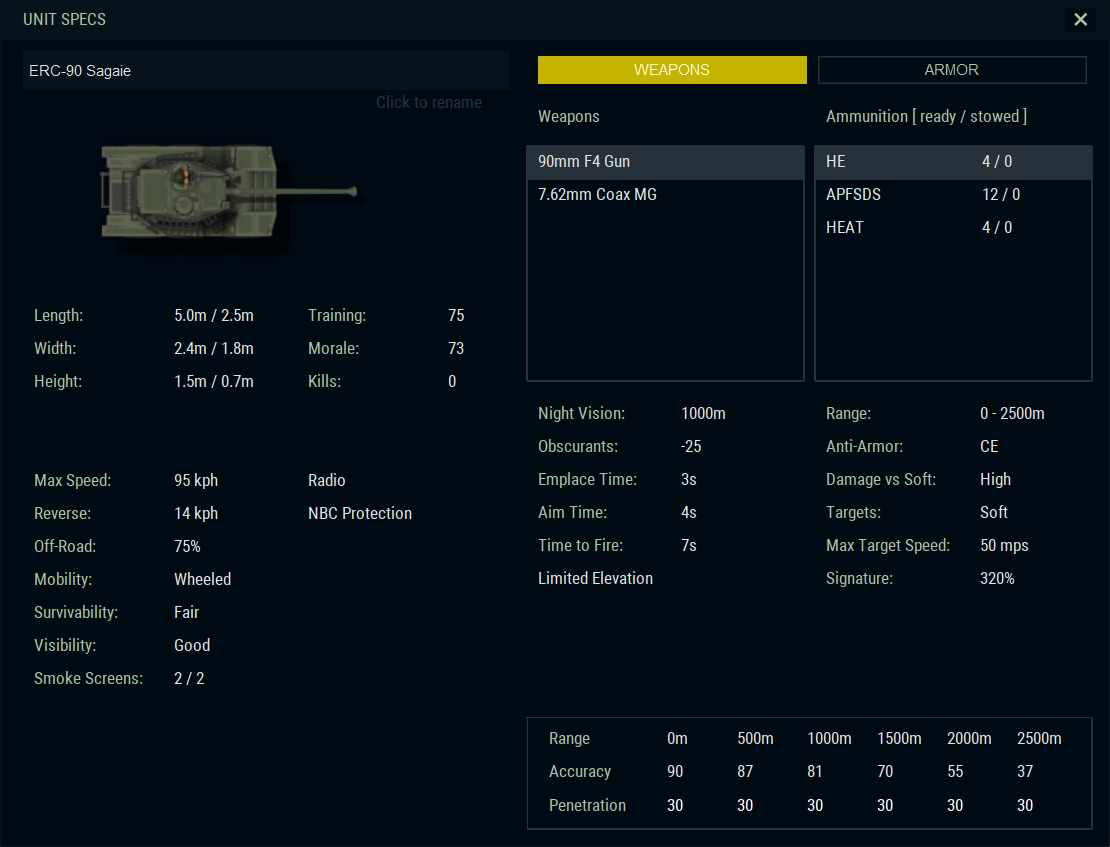
Mirage III: No longer required to serve purely as an interceptor, the Mirage III was quickly developed into a multi-role fighter by Dassault. The Mirage III E, ordered on April 6, 1960, was designed for low-altitude airstrikes. The fuselage was lengthened to accommodate the relevant electronic systems (navigation suite, Doppler radar), and was also equipped with a more powerful jet engine, the Atar 9C. Along with the companion Mirage III D two-seater and simplified Mirage 5, the Mirage IIIE accounted for the bulk of the 1,422 Mirage IIIs built by Dassault or under licence in Australia and Switzerland. After the outstanding Israeli success with the Mirage III, scoring kills against Syrian Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17 and MiG-21 aircraft and then achieving a formidable victory against Egypt, Jordan, and Syria in the Six-Day War of June 1967, the Mirage III's reputation was greatly enhanced.
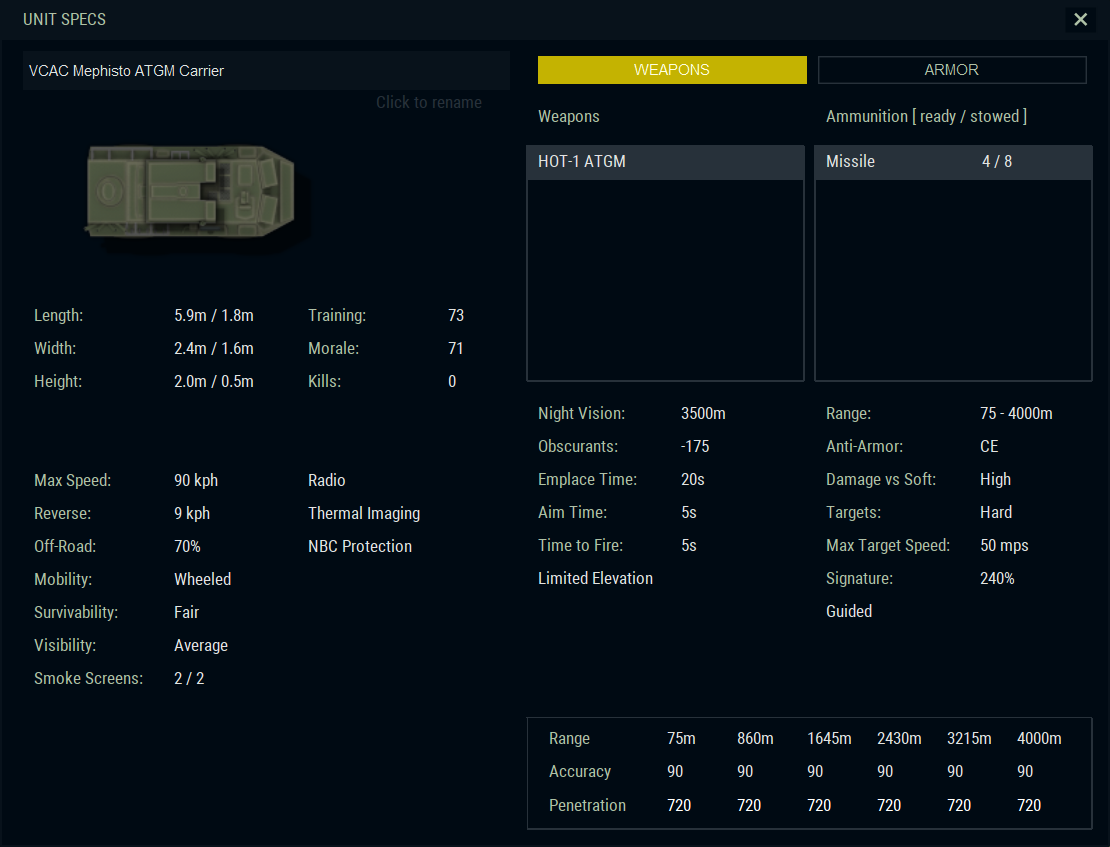
VAB VCAC ‘Mephisto’: VAB VCAC “Mephisto” (Module Élévateur Panoramique HOT Installé Sur Tourelle Orientable) is an antitank version of the most widespread troop carrier of the French army, the VAB. Able to fight against tanks with great autonomy (maximum range of 4000 meters), the VAB Mephisto is intended for anti-tank companies. It is based on simple and reliable chassis, which forms the base vehicle of French light armored infantry. This 4-wheel platform can be adapted to a wide array of purposes. Suitable for strategic movement due to a range of 1,200km, it is also transportable by air.
BELGIUM
AIFV-B IFV: In the mid-1960s, the United States Army studied a number of armored fighting vehicles that would replace the ubiquitous M113 and less successful M114 as well as take on a variety of new roles. Under military contract, FMC Corporation built two MICVs in 1967 with the designation XM765. These were based on the proven M113 hull modified to incorporate firing ports and a fully-enclosed weapon station. Although evaluated, the XM765 was nevertheless rejected in favor of other projects that eventually resulted in Bradley IFV. Further development of the XM765 by the company as a private venture resulted in the Product Improved M113A1, the first prototype of which was completed in 1970. This had a one-man turret with 25mm autocannon in the centre of the hull, behind the driver and engine, and spaced steel laminate armor was bolted onto the side and front, with the void filled with polyurethane foam. This vehicle was subsequently called the Armored Infantry Fighting Vehicle and the first country to order the AIFV was the Netherlands. In 1979, the government of Belgium followed suit and took on a fleet of 514 AIFV which would be produced locally.

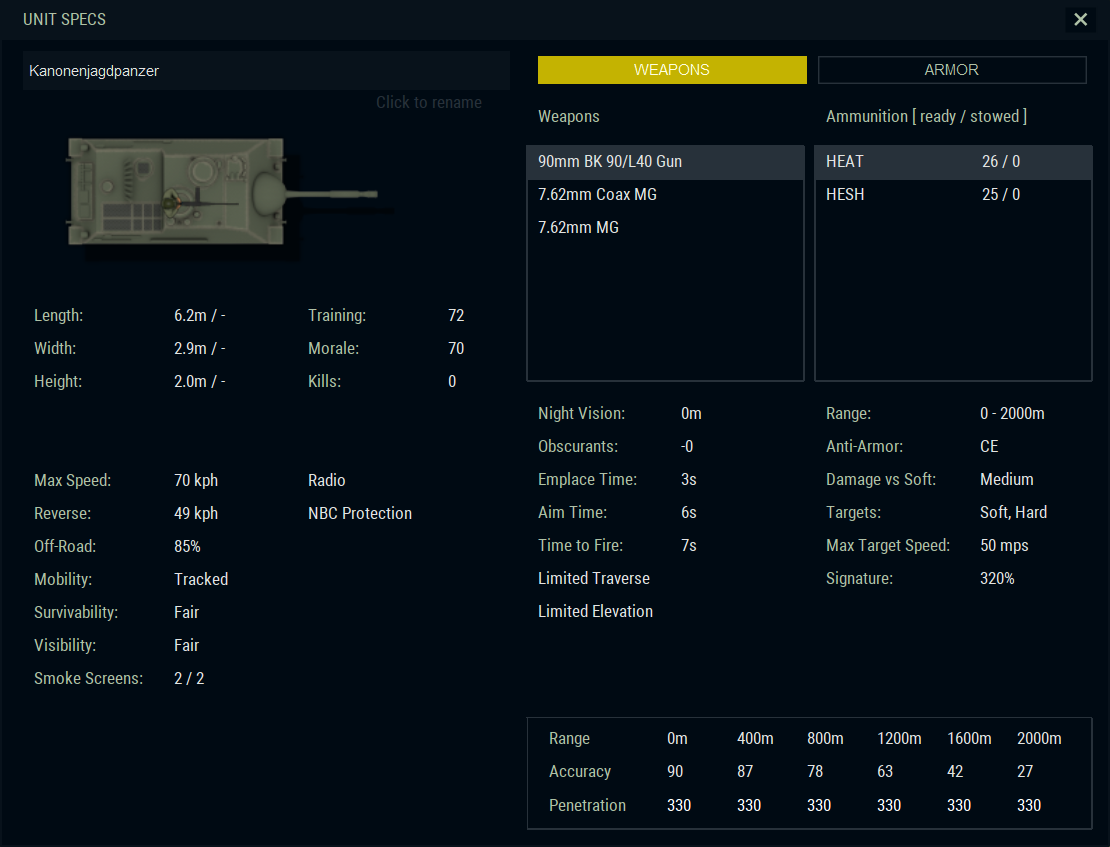
Kanonenjagdpanzer: The Kanonenjagdpanzer was a German Cold War tank destroyer equipped with a 90mm anti-tank gun, a design reminiscent of the Jagdpanzer IV tank destroyers of World War Two era. Between 1966 and 1967, 770 units were built for the Bundeswehr and further 80 of them were delivered to Belgian Army from April 1975 onward. It was light, fast and highly agile low-profile vehicle being powered by an MTU MB 837 500hp diesel-engine. With the 90mm gun becoming rapidly obsolete, some were converted to ATGM tank destroyers, others were pulled back to reserve units and in one way or another, they remained in service until the end of the Cold War.
M75 APC: The first of the “battle taxis”, the US Army’s trend setting M75 APC entered service in 1952. While the M75 shared many chassis and suspension components with the M41 Walker Bulldog light tank, it was not cost-effective as the approximate price of the vehicle was $72,000 (almost $700,000 today), which contributed to the early halting of production. Welded all-steel hull was relatively thick for an APC, up to 2 inches (50 mm) on the front, and 1 to 2.5 inches (25 to 38 mm) sides, roof and bottom, and therefore it weighted astonishing 42,000 pounds (19,051 kg) loaded. Due to changing demands and understanding of modern warfare, it was already showing its flaws by the time it reached the operational service. However, while it had a short career in the US Army, the M75s were given as military aid to Belgium, where they were used until the early 1980s.